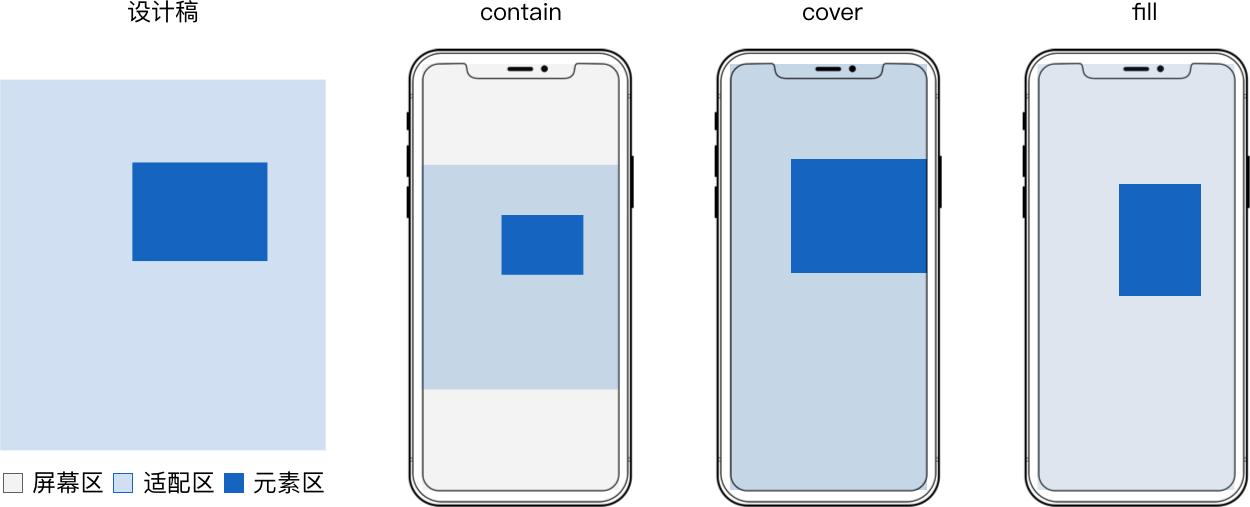
屏幕适配
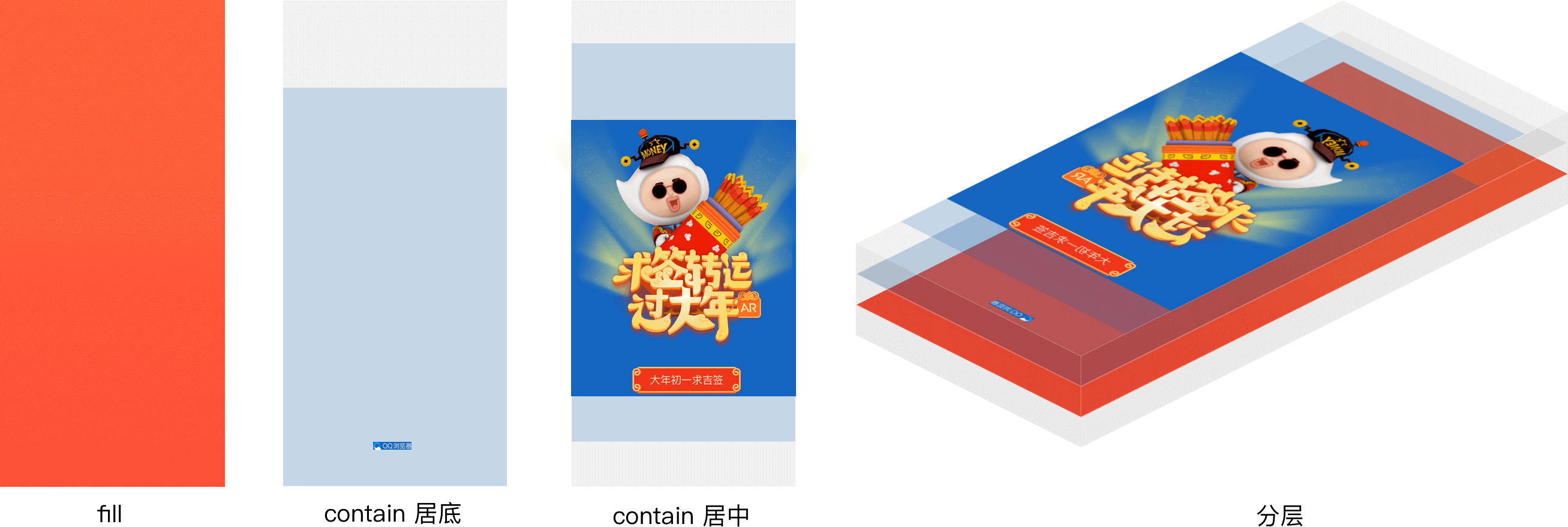
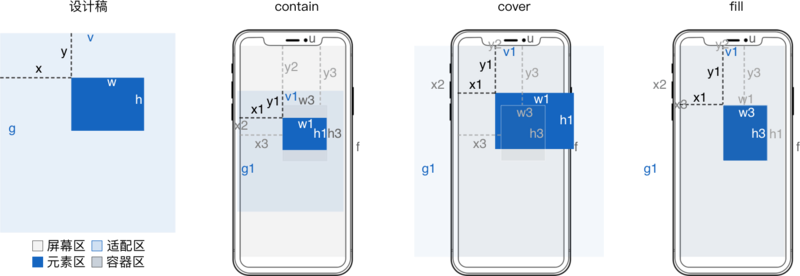
屏幕适配应当指内容 适配区 和 屏幕区 间的适配关系。 单屏适配有 contain、cover 或 fill,多屏常见是 依宽 。 contain 和 cover 还需要 定位 来处理留白和超出的内容。 而同一个 H5 里不同内容往往用不同适配方式,即 分层。
优选 CSS
- 页面加载后 js 往往需要延时至少 70ms 才能获取正确的 webview 宽高
- css 往往最先执行,且 cssom 的解析往往和 dom 在最开始并行构建
- js 会等待 dom 和 cssom 处理完后才能执行,而 css 只需等待 dom
- 相比 js 在切换横竖屏时要切换 2 次进程来重绘,css 无需切换
对于屏幕适配这类表现问题,能用 css 实现就应该用 css 实现。
整层适配
为确保各层元素同步缩放,不走样,每层的 适配区 应当等于设计稿大小。 直接的实现就是构造和 适配区 一样尺寸的 容器, 整层适配。 容器 内可以有若干个相同适配方式的 元素。 以 svg 实现为例:
<!doctype html>
<html>
<body>
<style>
.layer {
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
}
</style>
<!-- fill -->
<svg class="layer" viewBox="0 0 1080 1920" preserveAspectRatio="none"> <!-- 容器 -->
<rect x="0" y="0" width="1080" height="1920" fill="rgba(96,96,96,.08)"/> <!-- 元素 -->
</svg>
<!-- contain 居中 -->
<svg class="layer" viewBox="0 0 1080 1920" preserveAspectRatio="xMidYMid meet"> <!-- 容器 -->
<rect x="0" y="233" width="1080" height="1407" fill="#1565C0"/> <!-- 元素 -->
</svg>
<!-- contain 居底 -->
<svg class="layer" viewBox="0 0 1080 1920" preserveAspectRatio="xMidYMax meet"> <!-- 容器 -->
<rect x="444" y="1779" width="191" height="39" fill="#1565C0"/> <!-- 元素 -->
</svg>
</body>
</html>
实际效果:
整层适配** 实现简单,开发时直接读取设计稿值,可以满足大部分静态页面需求。 但在 h5 动画多的时候,就得考虑动画流畅,页面性能了。 用可替换元素如 <img> <object> <svg> 等做 容器,以及用背景图做 元素 的, 在应用 css 动画时有性能缺陷:
- 对 容器 内 元素 应用 css 动画会造成频繁重排和重绘,导致卡顿。
- 将和 适配区 尺寸相同的 容器 提升为合成层时所占内存过大,有多少层内存就翻多少倍。
为这些实现方案提升性能就要针对 容器 动画,并减小 容器 的尺寸,最好是和一层里所有 元素 的最小总面积相等,做到 **精简适配
精简适配
公式
推导过程见 H5 分层屏幕适配公式推导
设计稿
宽 v
高 g
适配前元素
横坐标 x
纵坐标 y
宽 w
高 h
适配后容器
横坐标 x3 = x*u/v
纵坐标 y3 = y*f/g
适配后元素
横坐标 x4 = m*u + (x - m*v)/w*w1 = m*v/w*w3 + (x - m*v)/w*w1
纵坐标 y4 = n*f + (y - n*g)/h*h1 = n*g/h*h3 + (y - n*g)/h*h1
宽 w3 = (w/v)*u
高 h3 = (h/g)*f
当 contain 方式适配时
缩放值 s = Math.min(f/g, u/v)
横向左留白占总留白 o = (m*v - x)/w
纵向上留白占总留白 p = (n*g - y)/h
当 cover 方式适配时
缩放值 s = Math.max(f/g, u/v)
横向左超出占总超出 o = (x - m*v)/w
纵向上超出占总超出 p = (y - n*g)/h
适配区
垂直居顶时 m = 0
垂直居中时 m = .5
垂直居底时 m = 1
水平居左时 n = 0
水平居中时 n = .5
水平居右时 n = 1
相比整层适配内存优化 (w3*h3)/(v1*g1) >= w*h/(v*g)
<img>实现示例
-
- 当设 max-width 为
w/v,max-height 为h/g时对应 contain 适配。 - 当设 min-width 为
w/v,min-height 为h/g时对应 cover 适配。 - 当设 width 为
w/v,height 为h/g时表示 fill 适配。 - contain 适配时,如果图片原始尺寸小于
max-width和max-height时,用zoom: 10放大或者直接修改图片原始尺寸。 - cover 适配时,如果图片原始尺寸大于
min-width和min-height时,用zoom: .1缩小或者直接修改图片原始尺寸。 - 因
topleft中百分比是相对屏幕宽u和高f的,对应m*u和n*f
- 当设 max-width 为
- 因
transform中百分比是相对适配后元素宽w1和高h1的,对应 `(mv + x)/ww1 和 (nf + y)/hh1<!doctype html> <html> <body> <style> img { /* min-width 和 min-height 构成了虚拟的容器 */ min-width: 50.37037037037037%; /* w3 = (w/v)*u 其中 w = 544,v = 1080 */ min-height: 7.395833333333333%; /* h3 = (h/g)*f 其中 h = 142,g = 1920 */ zoom: .1; /* x4 = m*u + (x - m*v)/w*w1 */ /* y4 = n*f + (y - n*g)/h*h1 */ position: absolute; left: 50%; /* m*u 其中 m = .5*/ top: 50%; /* n*f 其中 n = .5 */ transform: translateX(-48.34558823529412%) /* (x - m*v)/w*w1 其中 x = 277,m = .5,v = 1080,w = 544 */ translateY(378.8732394366197%); /* (y - n*g)/h*h1 其中 y = 1498,n = .5,g = 1920,h = 142 */ } </style> <img src="http://ui.qzone.com/544x142"/> <!-- 元素 --> </body> </html>
background 实现示例
background-size值为contain时对应 contain 适配。background-size值为cover时对应 cover 适配。background-size值为100% 100%时对应 `fill 适配。background-position百分比和op意义相同<!doctype html> <html> <body> <style> div { position: absolute; width: 50.37037037037037%; /* w3 = w/v*u 其中 w = 544,v = 1080 */ height: 7.395833333333333%; /* h3 = h/g*f 其中 h = 142,g = 1920 */ background: url(http://ui.qzone.com/544x142) no-repeat; /* 背景图做元素 */ background-size: cover; left: 25.64814814814815%; /* x3 = x/v*u 其中 x = 277, v = 1080 */ top: 78.02083333333333%; /* y3 = y/g*f 其中 y = 1498, g = 1920 */ background-position-x: -48.34558823529412%; /* o = (x - m*v)/w 其中 m = .5 , v = 1080,x = 277,w = 544*/ background-position-y: 378.8732394366197%; /* p = (y - n*g)/h 其中 n = .5 , g = 1920,y = 1498,h = 142*/ } </style> <div></div> <!-- 容器 --> </body> </html>
svg 实现示例
preserveAspectRatio的meetOrSlice为meet时对应 contain 适配。preserveAspectRatio的meetOrSlice为slice时对应 cover 适配。preserveAspectRatio值为none时对应 fill 适配。- 这里
preserveAspectRatio的meetOrSlice相对的是容器,不是 适配区 这里用transform来定位,而preserveAspectRatio的meetOrSlice固定为xMinYMin。<!doctype html> <html> <body> <style> svg { position: absolute; width: 50.37037037037037%; height: 7.395833333333333%; /* x4 = m*v/w*w3 + (x - m*v)/w*w1 */ /* y4 = n*g/h*h3 + (y - n*g)/h*h1 */ top: 0; left: 0; transform: translateX(99.26470588235294%) /* m*v/w*w3 其中 m = .5,v = 1080,w = 544 */ translateY(676.056338028169%); /* n*g/h*h3 其中 n = .5,g = 1920,h = 142 */ overflow: visible; } svg image { transform: translateX(-48.34558823529412%) /* (x - m*v)/w*w1 其中 x = 277,m = .5,v = 1080,w = 544 */ translateY(378.8732394366197%); /* (y - n*g)/h*h1 其中 y = 1498,n = .5,g = 1920,h = 142 */ } </style> <svg viewBox="0 0 544 142" preserveAspectRatio="xMinYMin meet"> <!-- 容器 --> <image width="544" height="142" xlink:href="http://ui.qzone.com/544x142"/> <!-- 元素 --> </svg> </body> </html>
辅助工具
手动计算百分比及写 css 很麻烦,可以借助 sass 等工具来辅助简化。 设计稿宽 v 高 g 一般是页面级常量。 只需读取设计稿里每个 元素 的横坐标 x 、纵坐标 y 、宽 w 和 高 h,然后工具生成 css 即可。 这下妈妈再也不用担心我还原问题、屏幕适配问题了。
文字处理
- 文字固定或单行不固定,
svg的text标签可以处理 - 文字固定或单行不固定还可以将文字转为图片
- 文字多行不固定,可以借助
svg的foreignObject嵌入普通div
方案对比
屏幕适配方案非常多,选哪种方式实现 整层适配 或 精简适配,下面是对比
| 缩放 | 定位 | 文字缩放 | 兼容 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| padding-top 百分比 | 只能依宽 | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ |
| viewport | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | 支持情况复杂 |
| object-fit | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | 移动端 android 4.4.4+ |
| svg preserveRatio | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 移动端 android 3.0+ |
| (max/min)-(width/height) | ✓ | ✓ | 固定文字 | ✓ |
| background-size | ✓ | ✓ | 文字转图片 | ✓ |
⚠️:此文章原站失效,无更多快照
原文标题:H5分层屏幕适配
原文链接:http://hai.li/2018/03/14/h5-screen-adaptation.html
原文快照:https://web.archive.org/web/20210923175012/http://hai.li/2018/03/14/h5-screen-adaptation.html
文章评论